 John O. Blackburn and Sam Cunningham
write about
Solar and Nuclear Costs — The Historic Crossover:
Solar Energy is Now the Better Buy
John O. Blackburn and Sam Cunningham
write about
Solar and Nuclear Costs — The Historic Crossover:
Solar Energy is Now the Better Buy
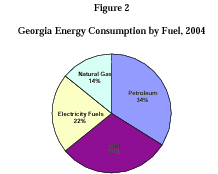
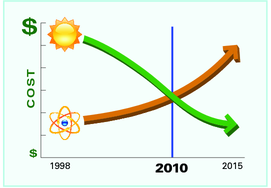
Solar photovoltaic system costs have fallen steadily for decades. They are projected to fall even farther over the next 10 years. Meanwhile, projected costs for construction of new nuclear plants have risen steadily over the last decade, and they continue to rise. In the past year, the lines have crossed in North Carolina. Electricity from new solar installations is now cheaper than electricity from proposed new nuclear plants. This new development has profound implications for North Carolina’s energy and economic future. Each and every stakeholder in North Carolina’s energy sector — citizens, elected officials, solar power installers and manufacturers, and electric utilities — should recognize this watershed moment.And North Carolina is north of Georgia, so Georgia should have more sun.
-jsq