 At the
EPA meeting in Waycross about the Seven Out Superfund site,
EPA, GA EPD, and state health officials also had information about
crossover contamination in Lowndes County.
At the
EPA meeting in Waycross about the Seven Out Superfund site,
EPA, GA EPD, and state health officials also had information about
crossover contamination in Lowndes County.
 Matthew J. Huyser, On-Scene Coordinator for U.S. EPA,
told me that before
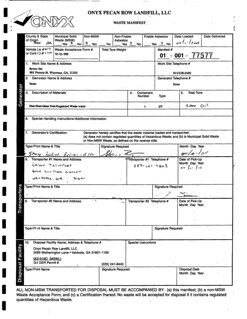
EPA shipped those 196,500 gallons of wastewater from Seven Out to the Pecan Row Landfill in Lowndes County
they had applied procedures that were supposed to ensure those liquids
were no longer toxic and had tested them to be sure.
He said he would send me the specifics on that.
I didn’t ask him whether
CSX toxic wastes were shipped to Lowndes County.
Matthew J. Huyser, On-Scene Coordinator for U.S. EPA,
told me that before
EPA shipped those 196,500 gallons of wastewater from Seven Out to the Pecan Row Landfill in Lowndes County
they had applied procedures that were supposed to ensure those liquids
were no longer toxic and had tested them to be sure.
He said he would send me the specifics on that.
I didn’t ask him whether
CSX toxic wastes were shipped to Lowndes County.
 Huyser also said EPA had checked the record of that receiving landfill
before sending anything there, and it had a good record.
He seemed surprised to learn Continue reading
Huyser also said EPA had checked the record of that receiving landfill
before sending anything there, and it had a good record.
He seemed surprised to learn Continue reading













