Very interesting projection of
Massachusetts Forest Impacts if Proposed Biomass Incinerators Are Allowed
by Chris Matera, P.E., and Ellen Moyer, Ph.D, P.E., with
GIS analysis and programming by Gordon Green:
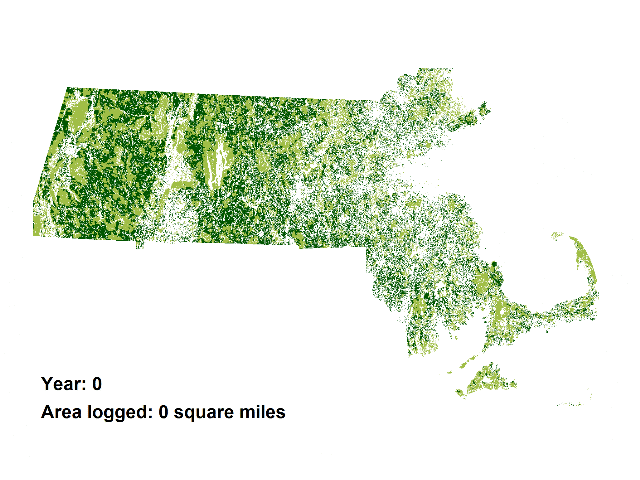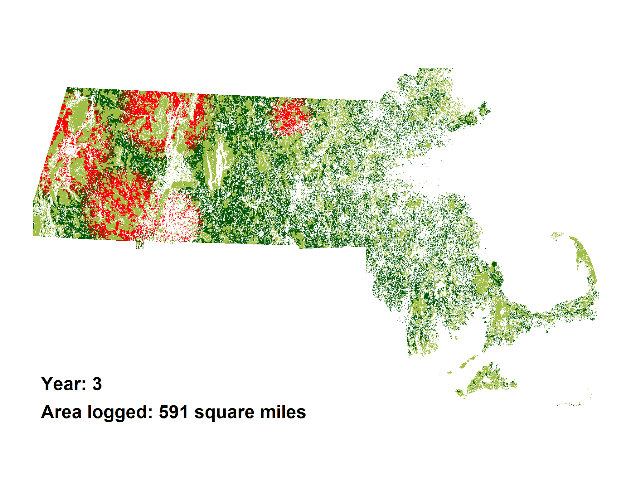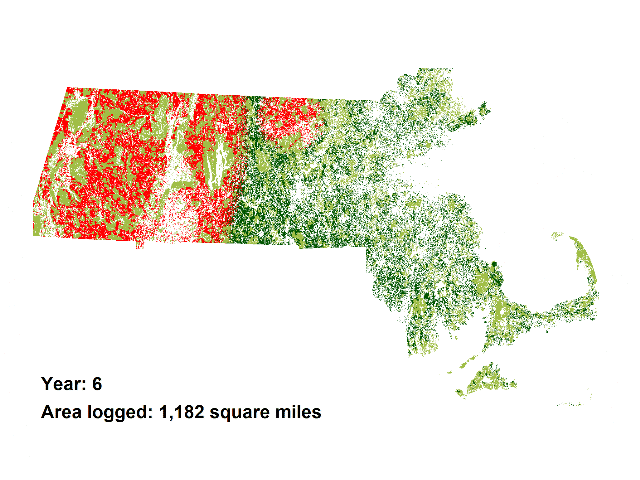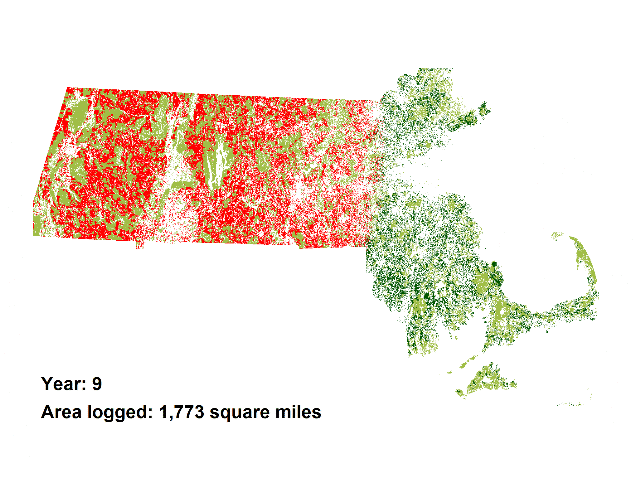
The animations add the demand for wood for 5 proposed biomass incinerators in Massachusetts to the current wood demand, which is mainly for lumber and cord wood. The animations demonstrate the land area in western and central Massachusetts that would be required to be logged to satisfy the total demand for these 5 plants which would add only about 1 percent to Massachusetts’ electrical generating capacity (see calculations below).
Quite a price for such a small percentage of electricity generation.
Solar, wind, and wave could generate far more electricity,
even in far northern Massachusetts.
And the animation above is a conservative projection.
Follow
the link for
…the extreme case where all forested land in central and western Massachusetts would be made available for biomass cutting – including rare species habitat, scenic landscapes, public “protected” land, and other protected open space. In this case, all forested land in central and western Massachusetts would be logged in only 16 years.
In Georgia, that would include places like Reed Bingham State Park.
-jsq
 Previously I promised to come back to the subject of whole trees.
Allan Ricketts asserted in the VLCIA meeting with concerned citizens
on 10 June 2010
that the biomass plant Wiregrass LLC proposed for Valdosta will never
burn whole trees because it would be economically unfeasible for it to do so.
While I have no doubt that Col. Ricketts is acting on the best information
given to him, there are reasons to be sceptical about what will happen
in the future.
Continue reading
Previously I promised to come back to the subject of whole trees.
Allan Ricketts asserted in the VLCIA meeting with concerned citizens
on 10 June 2010
that the biomass plant Wiregrass LLC proposed for Valdosta will never
burn whole trees because it would be economically unfeasible for it to do so.
While I have no doubt that Col. Ricketts is acting on the best information
given to him, there are reasons to be sceptical about what will happen
in the future.
Continue reading  Previously I promised to come back to the subject of whole trees.
Allan Ricketts asserted in the VLCIA meeting with concerned citizens
on 10 June 2010
that the biomass plant Wiregrass LLC proposed for Valdosta will never
burn whole trees because it would be economically unfeasible for it to do so.
While I have no doubt that Col. Ricketts is acting on the best information
given to him, there are reasons to be sceptical about what will happen
in the future.
Continue reading
Previously I promised to come back to the subject of whole trees.
Allan Ricketts asserted in the VLCIA meeting with concerned citizens
on 10 June 2010
that the biomass plant Wiregrass LLC proposed for Valdosta will never
burn whole trees because it would be economically unfeasible for it to do so.
While I have no doubt that Col. Ricketts is acting on the best information
given to him, there are reasons to be sceptical about what will happen
in the future.
Continue reading